Category: Sysadmin
Instalasi Virtualenv, Nodeenv Dan RVM Sebagai Development Environment
Virtualenv
Virtualenv adalah aplikasi untuk membuat membuat environment virtual Python terisolasi. Aplikasi ini membuat sebuah environment virtual yang mempunyai direktori instalasi sendiri, yang tidak berbagi library dengan environment Virtualenv lainnya dan dapat dikonfigurasi untuk tidak mengakses library yang diinstal secara global.
Instal pip di sistem operasi masing-masing, contohnya CentOS
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install -y python-pip
Instal virtualenv menggunakan pip
sudo pip install virtualenv
Buat environment virtual Python menggunakan virtualenv
Instalasi Let's Encrypt Dan Konfigurasi HTTPS Di Aplikasi Nginx Pada CentOS 7
Let’s Encrypt adalah Certificate Authority (CA) yang gratis dan terotomatisasi yang berjalan untuk kepentingan umum. Let’s Encrypt adalah sebuah layanan yang disediakan oleh Internet Security Research Group (ISRG). Prinsip-prinsip dasar dari Let’s Encrypt adalah gratis, otomatis, aman, transparan, terbuka, dan koperatif.
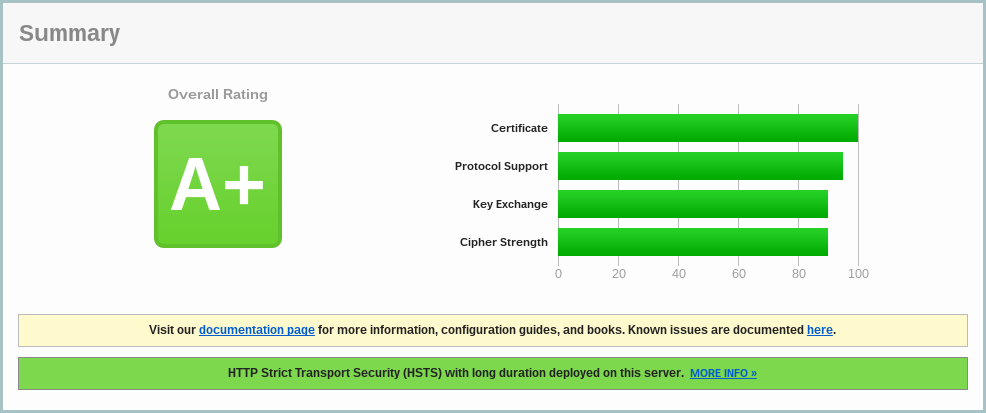
Instalasi Let’s Encrypt
Instalasi Let’s Encrypt
sudo yum -y install git bc
sudo git clone https://github.com/letsencrypt/letsencrypt /opt/letsencrypt
Buat sertifikat baru untuk domain example.com, sebelumnya hentikan dulu aplikasi Nginx
Konfigurasi Email Server Dengan SPF Dan DKIM Di Aplikasi Postfix Pada CentOS 7
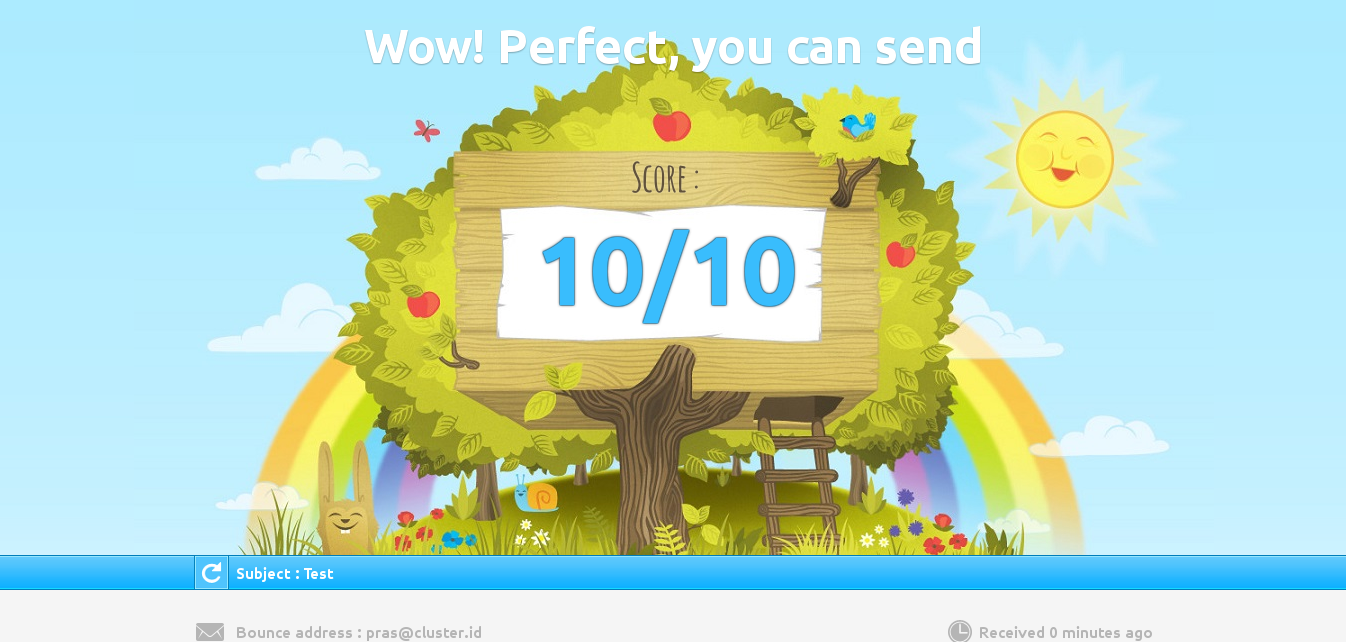
Setelah kita melakukan instalasi email server, cek skor email server di website Mail Tester. Salah satu contoh hasil pengecekan website tersebut sebagai berikut.
Content:
[Text]
[HTML]
[Source]
SpamAssassin:
[Score]
The famous spam filter SpamAssassin. A score below -5 is considered spam.
Authentication:
We check if the server you are sending from is authenticated
[SPF]
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email validation system designed to prevent email spam by detecting email spoofing, a common vulnerability, by verifying sender IP addresses.
[Sender ID]
Sender ID is like SPF, but it checks the FROM address, not the bounce address.
[DKIM]
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is a method for associating a domain name to an email message, thereby allowing a person, role, or organization to claim some responsibility for the message.
[DMARC record]
A DMARC policy allows a sender to indicate that their emails are protected by SPF and/or DKIM, and give instruction if neither of those authentication methods passes. Please be sure you have a DKIM and SPF set before using DMARC.
[PTR record]
Reverse DNS lookup or reverse DNS resolution (rDNS) is the determination of a domain name that is associated with a given IP address. Some companies such as AOL will reject any message sent from a server without rDNS, so you must ensure that you have one. You cannot associate more than one domain name with a single IP address.
[A record]
We check if there is a mail server (A Record) behind your hostname.
Errors:
Checks whether your message is well formatted or not.
[Image alternate tag]
alt attributes provide a textual alternative to your images. It is a useful fallback for people suffering from sight problems and for cases where your images cannot be displayed.
[HTML elements]
Checks whether your message contains dangerous html elements such as javascript, iframes, embed content or applet.
[URL shortener]
Checks whether your message uses URL shortener systems.
[List-Unsubscribe header]
The List-Unsubscribe header is required if you send mass emails, it enables the user to easily unsubscribe from your mailing list.
[Blacklist]
Matches your server IP address against 22 of the most common ipv4 blacklists.
Untuk meningkatkan skor, kita bisa memperbaiki konfigurasi email server dengan SPF dan DKIM
Membuat Virtual Machine di FreeBSD dengan bhyve dan vm-bhyve
Sejak FreeBSD 10.0-RELEASE, hypervisor bhyve (lisensi BSD) sudah menjadi bagian dari base system. Hypervisor adalah aplikasi yang bisa membuat dan menjalankan virtual machine atau yang biasa disebut guest di dalam sebuah sistem operasi. Guest yang didukung oleh bhyve cukup banyak, termasuk FreeBSD, OpenBSD, dan banyak distribusi Linux. Saat ini bhyve hanya mendukung konsol serial dan tidak bisa menampilkan konsol grafik. Bhyve membutuhkan prosesor baru yang mendukung Intel Extended Page Tables (EPT) atau AMD Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI), yang dikenal juga sebagai Nested Page Tables (NPT). Untuk Linux atau FreeBSD guest dengan vCPU (virtualCPU) membutuhkan dukungan VMX unrestricted mode (UG). Cara termudah untuk mengecek dukungan prosesor untuk bhyve adalah dengan menjalankan #dmesg# atau melihat isi /var/run/dmesg.boot untuk fitur POPCNT di baris Features dan EPT dan UG di baris VT-x. Panduan yang cukup lengkap untuk menggunakan bhyve dapat diakses di halaman ini
Playing with Ansible and FreeBSD
By default, FreeBSD doesn’t install a python package in its standard distribution. So, we need to install python, either manually or using ansible module.
$ ansible freebsd-host -m raw -a 'env ASSUME_ALWAYS_YES=YES pkg install python' -u root
Of course before we can use ansible we have to install public key authentication and enable SSH to root user in FreeBSD host from controller machine. FreeBSD install python in different path than Linux machine, so we must set variable for the python interpreter, either in host file or variable files.
Percona Server 5.6 Installation on CentOS 6
Percona Server 5.6 is the latest release of drop-in replacement for MySQL®. The new version offers all the improvements found in MySQL 5.6 Community Edition plus scalability, availability, backup, and security features found only in MySQL 5.6 Enterprise Edition, which requires a support contract from Oracle to access. Percona Server 5.6 is free, open source software which includes superior diagnostics and improved integration with other Percona software. In this documentation, I will show how to install Percona Server 5.6 on CentOS 6.
Beanstalkd Installation on CentOS 6
Beanstalkd is a simple, fast work queue. Its interface is generic, but was originally designed for reducing the latency of page views in high-volume web applications by running time-consuming tasks asynchronously. In this documentation, I will show how to install Beanstalkd on CentOS 6.
Install Beanstalkd from EPEL repository using yum
sudo rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install beanstalkd
Enable and start Beanstalkd service
sudo chkconfig beanstalkd on
sudo service beanstalkd start
Sensu Installation on CentOS 6
Sensu is often described as the “monitoring router”. Essentially, Sensu takes the results of “check” scripts run across many systems, and if certain conditions are met; passes their information to one or more “handlers”. Checks are used, for example, to determine if a service like Apache is up or down. Checks can also be used to collect data, such as MySQL query statistics or Rails application metrics. Handlers take actions, using result information, such as sending an email, messaging a chat room, or adding a data point to a graph. There are several types of handlers, but the most common and most powerful is “pipe”, a script that receives data via standard input. Check and handler scripts can be written in any language, and the community repository continues to grow! In this documentation, I will show how to install Sensu on CentOS 6.
InfluxDB Installation on CentOS 6
InfluxDB is an open-source, distributed, time series database with no external dependencies. In this documentation, I will show how to install InfluxDB on CentOS 6.
Download InfluxDB
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/influxdb/influxdb-latest-1.x86_64.rpm
Install InfluxDB
sudo rpm -ivh influxdb-latest-1.x86_64.rpm
Enable and start InfluxDB service
sudo chkconfig influxdb on
sudo service influxdb start
Reference: http://influxdb.com/download/
Fluent Treasure Data (TD) Agent Installation on CentOS 6
Fluentd is an open source data collector, which lets you unify the data collection and consumption for a better use and understanding of data. In this documentation, I will show how to install fluentd (td-agent) on CentOS 6.
Pre-installation: increase number of maximum file descriptors
ulimit -n
sudo vi /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
root soft nofile unlimited
root hard nofile unlimited
sudo reboot
Pre-installation: network kernel optimization
Elasticsearch on CentOS 6
Elasticsearch is a distributed restful search and analytics. In this documentation, I will show how to install Elasticsearch on CentOS 6.
Install Oracle Java
wget --header "Cookie: oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u31-b13/server-jre-8u31-linux-x64.tar.gz
sudo mkdir /opt/jre
sudo tar zxf server-jre-8u31-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /opt/jre
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java /opt/jre/jdk1.8.0_31/bin/java 2000
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/javac javac /opt/jre/jdk1.8.0_31/bin/javac 2000
sudo update-alternatives --display java
sudo update-alternatives --display javac
Import Elasticsearch GPG key
sudo rpm --import https://packages.elasticsearch.org/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
Add Elasticsearch repository
Varnish 4 on CentOS 6
Varnish Cache is a web application accelerator also known as a caching HTTP reverse proxy. You install it in front of any server that speaks HTTP and configure it to cache the contents. Varnish Cache is really, really fast. It typically speeds up delivery with a factor of 300 - 1000x, depending on your architecture. In this documentation, I will show how to install Varnish 4 on CentOS 6.
For first installation install Varnish repository
RVM for Managing Ruby Version on CentOS 6
RVM is a command-line tool which allows you to easily install, manage, and work with multiple ruby environments from interpreters to sets of gems. In this documentation I will show how to install RVM on CentOS 6.6.
Install Development Tools
sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools"
Install mpapis public key
sudo gpg2 --keyserver hkp://keys.gnupg.net --recv-keys 409B6B1796C275462A1703113804BB82D39DC0E3
or if failed
curl -sSL https://rvm.io/mpapis.asc | sudo gpg2 --import -
Install RVM for multiuser installation
Redis on CentOS 6
Redis is an open source, BSD licensed, advanced key-value cache and store. It is often referred to as a data structure server since keys can contain strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps and hyperloglogs. In this documentation, I will show how to install Redis on CentOS 6.
Install Development Tools
sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools"
Download and extract latest Redis package from http://redis.io/
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-2.8.19.tar.gz
tar zxf redis-2.8.19.tar.gz
Go to redis directory and run make
Open Source Phusion Passenger Module for Nginx on CentOS 6
Phusion Passenger is a web server and application server for your web apps which built upon Ruby or NodeJS. In this documentation I will show how to install open source version of Phusion Passenger on CentOS 6.6 using Ruby gem installation.
Check your Ruby location
which ruby
/usr/local/rvm/rubies/ruby-2.1.5/bin/ruby
In this tutorial I assume your Ruby is installed using RVM Install passenger using gem command
gem install passenger -V
Install passenger module for nginx
MongoDB on CentOS 6
MongoDB is the only database that harnesses the innovations of NoSQL (flexibility, scalability, performance) and builds on the foundation of relational databases (expressive query language, secondary indexes, strong consistency). In this documentation, I will show how to install MongoDB on CentOS 6.
Add MongoDB repository to yum
sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb.repo
[mongodb]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=http://downloads-distro.mongodb.org/repo/redhat/os/x86_64/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Install MongoDB
sudo yum install mongo-10gen mongo-10gen-server --exclude mongodb-org,mongodb-org-server
Add this to /etc/yum.conf to prevent MongoDB from being upgraded
Memcached on CentOS 6
Memcached is free & open source, high-performance, distributed memory object caching system, generic in nature, but intended for use in speeding up dynamic web applications by alleviating database load. Memcached is an in-memory key-value store for small chunks of arbitrary data (strings, objects) from results of database calls, API calls, or page rendering. In this documentation I will show how to install memcached using yum package manager with Atomicorp repository.
Install the latest Atomicorp repository from http://www6.atomicorp.com/channels/atomic/centos/6/x86_64/RPMS/
Start Your Own Documentation Blog
I am trying to write again after some month was absent from touching any electronic notes (blogs). Actually I wanted to do it from a long time ago but I was afraid don’t have any material with qualities to be written. In reality, I realized that I have been encountering events that I must write about. After so long trying to make up my mind and gather my courage, I finally be able to put some ideas into my writing, starting with this re-introduction.
Upgrade Ghost
I have run Ghost for quite some time now and I have been through two upgrade process so I think it will be a good idea to save a procedure for easy upgrading. I found the instruction here.
###Manually upgrade Ghost
I usually use manual upgrade method because I don’t inspect the automatic scripts yet if it is compatible with my installation.
# cd /var/www/html/ghost
# mkdir temp
# cd temp/
# curl -L -O https://ghost.org/zip/ghost-latest.zip
# unzip ghost-latest.zip
# cd ..
# cp temp/*.md temp/*.js temp/*.json .
# rm -R core
# cp -R temp/core .
# cp -R temp/content/themes/casper content/themes
# npm install --production
# rm -R temp
# su ghost -c /var/www/html/ghost/starter.sh -s /bin/sh
###Reference http://www.howtoinstallghost.com/how-to-update-ghost/
Puppet Master-Agent Installation on FreeBSD
Puppet is a software which can automate configuration and management of machines and software running on them. This tool has great benefits for system administrator because it helps sysadmin to be the dream of every sysadmin, a lazy sysadmin. Puppet has great support for many operating system. Unfortunately its installation on my favourite OS, FreeBSD, is not so smooth. An introduction of Puppet installation which I found in BSD Magazine January 2012 edition is a starting point but I have to make some modification due to some of deprecated configurations. So, here I want to show you how to install and configure the basic of Puppet in FreeBSD in its master-agent scenario. ##Let’s start… ###Puppet benefits:
Installing MySQL Server on FreeBSD
Installation using FreeBSD ports
Login as root, then to make sure our server’s hostname can be identified locally we need to edit /etc/hosts.
# ee /etc/hosts
::1 localhost localhost.example.com
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.example.com
192.168.1.11 host.example.com
Install MySQL Server with following command.
# cd /usr/ports/databases/mysql56-server
# make -D BUILD_OPTIMIZED install clean
# rehash
After installation finished, run script for installing main database and tables used by MySQL.
# mysql_install_db --user=mysql –basedir=/usr/local/
Run following command to start MySQL daemon and create password for MySQL’s root. # mysqld_safe & # mysqladmin -u root password ’localpassword' # mysqladmin -u root -h host.example.com password ‘remotepassword’
Installing Cyrus SASL Server on FreeBSD
###Instalation using FreeBSD ports
Login as root then enter ports directory of Cyrus SASL and run following command.
# cd /usr/ports/security/cyrus-sasl2-saslauthd
# make config ; make install clean
# rehash
Create file smtpd.conf in directory /usr/local/lib/sasl2/.
# ee /usr/local/lib/sasl2/smtpd.conf
Then add following lines.
pwcheck_method: saslauthd
mech_list: plain login
Edit file rc.conf so that SASL Authentification server can start at boot time.
# ee /etc/rc.conf
saslauthd_enable="YES"
saslauthd_flags="-a pam"
if you want to use other authentication mechanism such as LDAP, use following flags.
Installing Apache HTTP Server on FreeBSD
###Installation using FreeBSD ports
Login as root, then to make sure our server’s hostname can be identified locally we need to edit /etc/hosts.
# ee /etc/hosts
::1 localhost localhost.example.com
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.example.com
192.168.1.11 host.example.com
Install Apache HTTP Server using following command, choose default for options, select OK.
# cd /usr/ports/www/apache22
# make config; make install clean
# rehash
After installation proses finished, change Apache configuration file.
# ee /usr/local/etc/apache22/httpd.conf
ServerAdmin you@example.com
ServerName host.example.com:80
To enable SSL support, uncomment following line.
Heartbeat Using Different UDP Ports for Different Clusters on Same Network
Heartbeat is a daemon that provides cluster infrastructure (communication and membership) services to its clients. This allow clients to know appearance or disappearance of peer processes on other machines and to easily exchange message with them.(Heartbeat - Linux-HA)
Heartbeat clusters work only one on same network so if we setup different cluster (different authkeys) on same network it will show up as an error in log file. We can still setup more than one cluster in same network by setting different communication port for heartbeat.
Git Tutorial
Git is a distributed version control system version control system track history of a collection of files and includes the functionality to revert to another version.
Distributed version control system does not necessarily have a central server which stores data.
User can copy existing repository (cloning).
Every clone contains full history of the collection of files and a clone repository has the same functionality as the original repository.
Users with sufficient authorization can push changes from their local repositories to remote repositories, they can also fetch or pull changes from other repositories to their local Git repository.
DRBD: Extend DRBD Disk Online
When using DRBD, we can grow DRBD disk online so we do not need to disturb the production process we have in the server. The requirement to this feature is the backing block device can be resized online so it is possible to resize the DRBD disk. There are two criterias that must be filled.
####1. The backing device must be managed by a logical volume manager such as LVM ####2. The resource must currently be in the Connected connection state. First, we need to grow the backing device on both nodes and make sure only one node in Primary node.
SMTP: Debugging SMTP with TLS/SSL and Auth
SMTP use TLS/SSL to secure connection to server and AUTH so only authenticated user can use the SMTP service. This tutorial will show steps to debug SMTP TLS/SSL and AUTH from Linux/Unix terminal.
-
encode your login information in base64, the following perl command which requires MIME::Base64 will do encoding
perl -MMIME::Base64 -e 'print encode_base64("\000your_username\000your_password")' # example output # AHlvdXJfdXNlcm5hbWUAeW91cl9wYXNzd29yZA== -
connect to smtp server
# normal non-secured SMTP $ telnet smtp.yourdomain.com 25 # TLS connection, check STARTTLS support with EHLO command $ telnet smtp.yourdomain.com 25 220 SMTP banner EHLO smtp.yourdomain.com 250 SMTP banner 250-smtp.yourdomain.com 250-PIPELINING 250-SIZE 36360000 250-VRFY 250-ETRN 250-STARTTLS 250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES 250-8BITMIME 250 DSN quit $ openssl s_client -starttls smtp -crlf -connect smtp.yourdomain.com:25 # SSL connection $ openssl s_client -crlf -connect smtp.yourdomain.com:465 -
check AUTH support with EHLO command
LVM: Adding New Physical Volume to Volume Group
Linux LVM is a logical volume manager for Linux kernel. Logical volume manager provides method of allocation space in mass storage device that more flexible than traditional partitioning scheme. Logical volume manager can create, resize, and combine partitions, potentially without interrupting system. (Wikipedia)
schema: new device /dev/sda
1. create needed partitions, label them with 8e (Linux LVM)
# fdisk /dev/sda
2. format partitons
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda1
3. create physical volume
# pvcreate /dev/sda1
4. extend existing volume group
# vgextend VolGroup00 /dev/sdb1
5. extend existing logical volume
extend LogVol01 to 16GB
# lvextend -L 16G /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol01
adding 1GB to LogVol01
# lvextend -l+1G /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol01
6. resize logical volume to new size
# resize2fs /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol01
7. create new logical volume
create new logical volume with size 16GB
# lvcreate -L 16GB -n LogVol02 VolGroup00
create new logical volume with all free space
# lvcreate -l+100%FREE -n LogVol02 VolGroup00
8. format new logical volume
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol02
Reference: http://sujithemmanuel.blogspot.com/2007/04/how-to-add-disk-to-lvm.html
iSCSI+LVM: Automatically Enable Volume Group Contain iSCSI Disk Physical Volume
When using iSCSI and LVM, sometimes we have to manually enable iSCSI disk that used as a physical volume in LVM. This is because LVM service is started earlier than iSCSI service so the iSCSI disk containing the physical volume is not present yet. Solution to this problem is to enable lvmetad in /etc/lvm/lvm.conf. The lvmetad is “LVM metadata daemon” that acts as in-memory cache of LVM metadata gathered from devices as they appear in the system. Whenever a block device appears and has PV label on it, it is automatically scanned via an udev rule. This update the lvmetad daemon with the LVM metadata found. Once the VG is complete (all the PVs making up the VG are present), the VG is activated. The lvmetad daemon is required for this LVM event-based autoactivation to work and the iSCSI disk must be present in the system after boot time.
Installing Postfix with Auth SASL and LDAP Support on FreeBSD
Install packages using FreeBSD port.
1. Install postfix
# Options for postfix-2.11.0,1
_OPTIONS_READ=postfix-2.11.0,1
_FILE_COMPLETE_OPTIONS_LIST=BDB CDB INST_BASE LDAP_SASL LMDB MYSQL NIS OPENLDAP PCRE PGSQL SASL2 SPF SQLITE TEST TLS VDA DOVECOT DOVECOT2 SASLKRB5 SASLKMIT
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=BDB
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=CDB
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=INST_BASE
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=LDAP_SASL
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=LMDB
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=MYSQL
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=NIS
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=OPENLDAP
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=PCRE
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=PGSQL
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=SASL2
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=SPF
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=SQLITE
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=TEST
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=TLS
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=VDA
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=DOVECOT
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=DOVECOT2
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=SASLKRB5
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=SASLKMIT
2. install openldap
# Options for openldap-client-2.4.38
_OPTIONS_READ=openldap-client-2.4.38
_FILE_COMPLETE_OPTIONS_LIST=FETCH
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=FETCH
3. install cyrus-sasl2
# Options for cyrus-sasl-2.1.26_4
_OPTIONS_READ=cyrus-sasl-2.1.26_4
_FILE_COMPLETE_OPTIONS_LIST=ALWAYSTRUE AUTHDAEMOND KEEP_DB_OPEN OBSOLETE_CRAM_ATTR BDB MYSQL PGSQL SQLITE2 SQLITE3 CRAM DIGEST LOGIN NTLM OTP PLAIN SCRAM
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=ALWAYSTRUE
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=AUTHDAEMOND
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=KEEP_DB_OPEN
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=OBSOLETE_CRAM_ATTR
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=BDB
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=MYSQL
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=PGSQL
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=SQLITE2
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=SQLITE3
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=CRAM
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=DIGEST
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=LOGIN
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=NTLM
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=OTP
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=PLAIN
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=SCRAM
4. install cyrus-sasl2-saslauthd
# Options for cyrus-sasl-saslauthd-2.1.26
_OPTIONS_READ=cyrus-sasl-saslauthd-2.1.26
_FILE_COMPLETE_OPTIONS_LIST=BDB HTTPFORM OPENLDAP
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=BDB
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=HTTPFORM
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=OPENLDAP
5. install postfwd
# Options for postfix-postfwd-1.32_1
_OPTIONS_READ=postfix-postfwd-1.32_1
_FILE_COMPLETE_OPTIONS_LIST=DOCS EXAMPLES POSTFWD2
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=DOCS
OPTIONS_FILE_SET+=EXAMPLES
OPTIONS_FILE_UNSET+=POSTFWD2
6. configure /usr/local/lib/sasl2/smtpd.conf
log_level: 3
pwcheck_method: saslauthd
mech_list: PLAIN LOGIN
7. configure /usr/local/etc/saslauthd.conf
ldap_servers:
ldap_bind_dn:
ldap_bind_pw:
ldap_search_base:
ldap_auth_method: ssha
ldap_time_limit: 4
ldap_filter:
8. configure /usr/local/etc/postfix/main.cf
mtpd_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtpd_sasl_local_domain =
smtpd_sasl_authenticated_header = yes
broken_sasl_auth_clients = yes
smtpd_sasl_path = smtpd
smtp_sasl_type = cyrus
smtpd_sasl_security_options = noanonymous
smtpd_recipient_restrictions =
permit_mynetworks,
permit_sasl_authenticated,
reject_unauth_destination
9. configure /usr/local/etc/postfwd.conf
id=RULE001
sasl_username=~/^(\S+)$/
action=rcpt(sasl_username/200/3600/DEFER Too much emails for $$sasl_username)
10. configure /etc/rc.conf
postfix_enable="YES"
saslauthd_enable="YES"
saslauthd_flags="-a ldap"
postfwd_enable="YES"
Reference: http://ashterix.blogspot.com/2008/10/freebsd-postfix-sasl-openldap.html
FreeBSD Check TCP/UDP Open Port or Services
In this short tutorial I will show how to check TCP/UDP open port or services in FreeBSD box. For checking open port or services which uses port in FreeBSD simply issue the following commands.
-
check TCP connection
sockstat -Ptcp -
check UDP connection
sockstat -PudpCombine with grep to search port used by specific service or service which using specific port.
-
use grep to get service or port
sockstat -Ptcp | grep <port number> sockstat -Ptcp | grep -i <service name> sockstat -Pudp | grep <port number> sockstat -Pudp | grep -i <service name>
DRBD: Troubleshooting and Error Recovery of Hard Drive Failure or Replacement
DRBD refers to block devices designed as a building block to form high availability cluster. This is done by mirroring a whole block device via an assigned network. DRBD can be understood as network based RAID-1. (DRBD)
Sometimes we have a disk failure on hard drive which contains DRBD backing device. The following steps can be used to replace or recover the failed drive.
1. detach drbd resource from broken backing storage
# drbdadm detach <resource>
2. check state of drbd disk
# drbdadm dstate <resource>
Diskless/UpToDate
3. if using internal meta data, bind DRBD device to new hard disk
# drbdadm create-md <resource>
# drbdadm attach <resource>
4. if using external meta data DRBD unable to recognize hard drive was swapped, need additional step
# drbdadm create-md <resource>
# drbdadm attach <resource>
# drbdadm invalidate <resource>
Reference: http://www.drbd.org/users-guide-8.4/ch-troubleshooting.html
DRBD: Manual Split Brain Recovery
Split Brain in DRBD is a condition where each host think that resource in another host is outdated, thus synchronization won’t be occured. This condition often occurs because of network or power failure which is indicated by these variables:
log: Split-Brain detected, dropping connection
connection-state: StandAlone/WFConnection
To manually recover the cluster from split brain condition, the following steps is required.
1. on victim connection state must be StandAlone
# drbdadm disconnect <resource>
2. set victim as secondary
# drbdadm secondary <resource>
3. reconnect victim
# drbdadm connect --discard-my-data <resource>
4. on the survivor, if the connection state StandAlone enter following command
# drbdadm connect <resource>
Reference: http://www.drbd.org/users-guide-8.4/s-resolve-split-brain.html
Find A Virtual Machine by MAC Address with VSphere Client and PowerCLI
It is usual task to find someone computer by its MAC address when there is an issue related to his computer in the local network. The common case is IP conflict or network abuse. But, if the MAC Address shows that machine is one of many scattered VMware virtual machine out there, how do we find it?
####vSphere Client If you have an VMware ESX or ESXi server, vSphere Client is tool to manage your virtual machines from remote computer. But, vSphere Client cannot tell the MAC Address of virtual machines from version 10 or higher and to find virtual machine based on MAC Address we must open the virtual machine Setting one by one. It is still possible when there are few virtual, but it is exhausting when we have many virtual machine.
Installing Zimbra Collaboration Server 8 FOSS on CentOS 6.5
Zimbra is a well known collaboration suite which includes email, calendaring, file sharing, activity streams, social communities and more. The most popular product from Zimbra is Zimbra Collaboration Server. Zimbra Collaboration Server comes with two version: Network Edition and Open Source Edition (FOSS). This documentation shows a simple way to install Zimbra Collaboration Server Open Source Edition in CentOS 6.5.
###Getting Started
Prepare the system
# yum update
Disable SELinux
Installing Icinga on Scientific Linux 6.4
Icinga is a well-known server or network monitoring that runs in many Unix/Linux distribution. Server/Network monitoring is an essential part of Network Operations Center because by monitoring network engineers can always get the feedback and status from network and production servers. This is a simple documentation of Icinga installation in Scientific Linux 6.4 server. ###Getting started Before we install icinga, it best to keep our system updated.
# yum update
Search icinga package using yum search in RPMForge repository.
Installing Cacti on Scientific Linux 6.4
Cacti is a network graphic monitoring tools which used the potential of RRDTool. RRDTool is a data logging and graphing system for time series data. Cacti can show us a real time performance of network or servers which make this software become one of the most popular open source monitoring software.
 ###Getting Started
Always update your box before we install new software.
###Getting Started
Always update your box before we install new software.
# yum update
Install dependencies for cacti.
Installing Postfix and Dovecot on CentOS 6.5
Hello, I want to share a documentation how to setup a mail server using CentOS 6.5 using Postfix as SMTP server and Dovecot as IMAP/POP3 server. Postfix is a well known Message Transfer Agent that mostly used today and Dovecot is also one of the widely used Mail User Agent. ###Preparing The Machine In this documentation we use a CentOS 6.5 server and before we start, let’s update the system.
# yum update
A mail server needs to have a MX record in its DNS, so make sure we have that. It is also a good thing to set the PTR record pointing to our domain too.
Installing Nginx on CentOS 6.5
CentOS community now works together with Redhat alongside Fedora. It’s good news. So, we can hope to get a better software and support for next release of our beloved CentOS. As one of Linux (CentOS) fan, I want to share my experience installing nginx (engine-x) in CentOS 6.5. My VPS was installed as minimal server and then I added new packages, such as “Development tools” group and new repos (EPEL, CentALT).
Installing BIND DNS Server on CentOS 6.5
When we rent a VPS, we will get a public IP address so we can access our VPS from anywhere in this world. But, sometimes we want a better way to access our VPS using Domain Name. We will have to rent a domain name from a Domain Name Registrar and then set up our Name server so that our domain name refer to our IP address. There is usually an easier way by using our registrar control panel to set up NS records. But, if you still want to set up your own Name server, I hope this documentation will be useful for you.
Category: Jekyll Update
Welcome to Jekyll!
You’ll find this post in your _posts directory. Go ahead and edit it and re-build the site to see your changes. You can rebuild the site in many different ways, but the most common way is to run jekyll serve, which launches a web server and auto-regenerates your site when a file is updated.
To add new posts, simply add a file in the _posts directory that follows the convention YYYY-MM-DD-name-of-post.ext and includes the necessary front matter. Take a look at the source for this post to get an idea about how it works.
Category: Python
Re-Introduction to Python
Python is one of the programming languages which can claim to be both simple and powerful.
Python is an easy to learn, powerful programming language with efficient high-level data structures and a simple but effective approach to object oriented programming. Python’s elegant syntax and dynamic typing, together with its interpreted nature, make it an ideal language for scripting and rapid application development in many areas in many platforms.
Guido van Rossum, the creator of the Python language, named the language after the BBC show “Monty Python’s Flying Circus”.
Category: Idea
The End of Generation of Tinkerers
The Prologue
My college was the only college I know that gave the chance to its students to run the college network infrastructures. It encourages the students to study more outside their respective fields and share the knowledge in a community. Only a handful of people know that in the early days, the network infrastructure of my college, was built through the hands of its own students and the tradition to maintain it has been passed through the new generation of students.
Category: Engineering
Akuisisi Data Sensor LM35 dengan Arduino
Ini adalah tulisan pertama di blog ini yang membahas tentang hardware dan yang pertama menggunakan bahasa Indonesia. Sensor temperatur LM35 (datasheet) adalah sensor IC (Integrated Circuit) yang memberikan respon terhadap perubahan temperatur di sekitarnya dalam bentuk keluaran tegangan analog. Sensor temperatur LM35 bekerja pada tegangan 4 sampai 30V dan mempunyai respon linear 10mV/derajat Celcius pada rentang -55 sampai 150 derajat Celcius berdasarkan datasheet yang tersedia. Akuisisi data menggunakan sensor temperatur ini adalah percobaan sederhana yang bisa dikembangkan untuk perangkat Internet of Thing. Garis besar percobaan ini adalah keluaran dari sensor LM35 dibaca oleh Arduino melalui pin input analog (A0). Pin input analog Arduino mengeluarkan nilai dengan resolusi 10 bit untuk rentang 0 sampai 5V. Untuk mengetahui tegangan keluaran dari sensor LM35, diperlukan perhitungan berikut ini,
Category: Development
Getting Started with Hugo
Step 1. Install Hugo
Goto hugo releases and download the appropriate version for your os and architecture.
Save it somewhere specific as we will be using it in the next step.
More complete instructions are available at installing hugo
Step 2. Build the Docs
Hugo has its own example site which happens to also be the documentation site you are reading right now.
Follow the following steps:
- Clone the hugo repository
- Go into the repo
- Run hugo in server mode and build the docs
- Open your browser to http://localhost:1313
Corresponding pseudo commands:
Category: Golang
Getting Started with Hugo
Step 1. Install Hugo
Goto hugo releases and download the appropriate version for your os and architecture.
Save it somewhere specific as we will be using it in the next step.
More complete instructions are available at installing hugo
Step 2. Build the Docs
Hugo has its own example site which happens to also be the documentation site you are reading right now.
Follow the following steps:
- Clone the hugo repository
- Go into the repo
- Run hugo in server mode and build the docs
- Open your browser to http://localhost:1313
Corresponding pseudo commands:
Category: Computational Material
Quantum Espresso 5.0.3 Using Intel Math Kernel Library 11.0 Optimization
Quantum Espresso is a software for electronic-structure calculations and materials modeling at the nanoscale. The installation of Quantum Espresso is quite easy because it includes external libraries which it needs. But we are encouraged to install Quantum Espresso using our own machine optimized external libraries such as Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS), Linear Algebra Package (LAPACK), Scalable LAPACK (SCALAPACK), and Fastest Fourier Transform in the West (FFTW). ###External Libraries There are several repositories or development teams which provide external libraries. For example is Netlib which provides BLAS, LAPACK, and SCALAPACK. But, for machines with Intel processor, maybe the best external libraries out there is Intel® Math Kernel Library which has a non-commercial version as standalone or included in Intel® Parallel Studio XE 2013 for Linux that can be downloaded in Intel Non-Commercial Software Development. Intel® Math Kernel Library provides BLAS, LAPACK, SCALAPACK, and even FFTW interfaces. ###Getting Started My test machine is Supermicro X9DRD-7LN4F which has Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2660 0 @ 2.20GHz with 8 cores and 16 threads and 64 GB RAM. For compilers I will be using Intel compilers which is included in Intel® Parallel Studio XE 2013 for Linux and OpenMPI for parallelization. ####Installing Intel® Parallel Studio XE 2013 for Linux
Category: University
Final Project
I have reached the eight semester in my undergraduate study and it means this semester I have to finish a final project (Tugas Akhir, ID) as a requirement to graduate. Actually I don’t really into my final project’s topic. There are many factors behind it. In the new curriculum, my department decide to give a final project to a team consist of two students. This is a good news because the possibility of student who will graduate is increased. But, this is somewhat a setback for me. I don’t usually work in a team and for my final project I want to do a final project which is a original, only for me, my own final project. The requirement that a final project must be done by a team makes me don’t feel that this is really my own final project.
